Risk inside confined space
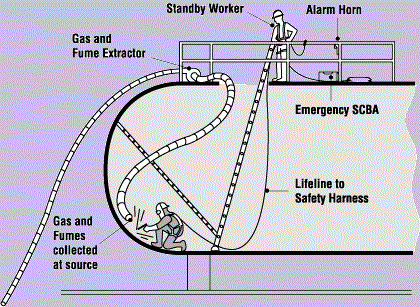
risk inside confined space
Risk inside confined space is common. Performing tasks in confined spaces may result in workers being exposed to a variety of hazards, depending on the nature of the work to be performed, the equipment to be used, the presence of hazardous substances or microorganisms or the geometry and configuration of the confined space itself. Thus, risks in confined spaces can be subdivided into two global categories. You can see also this What is confined space and its characteristics.
1. Mechanical Risks
2. Specific Risks
Now we will discuss mechanical and specific risks one by one.
1. Mechanical Risks
Mechanical Risks are caused by several physical factors, such as the characteristics of the confined space, its structural stability, the type and duration of the work to be done, among others. Examples of mechanical hazards, Risk inside confined space but not limited to:
- Risk of falling from a height.
- Risk of drowning.
- Electrocution risk.
- Hearing loss.
- Risk of a partial or total collapse of structures.
- Risk of falling objects/debris.
- Risk of prolonged and excessive fatigue.
2. Specific Risks
Specific risks are directly related to atmospheric, environmental, chemical and biological conditions within the confined space. Examples of specific risks, but not limited to:
Choking Hazard
The below table is defining risks at different concentrations of oxygen level inside confined space.
| Concentration (%) | Risks |
| 21% | Normal O2 concentration in the air |
| 18% | Loss of muscle coordination and acceleration of breathing rhythm |
| 17% | Loss of consciousness |
| 12-16% | Dizziness, headache, loss of muscle coordination and loss of consciousness |
| 6-10% | Nausea, loss of consciousness and death |
Chemical Hazards
| Examples of Toxic Gas | Dangers / Risks / Possible effects |
| Hydrochloric Acid (HCL) | Corrosive, Toxic – affects the respiratory tract |
| Hydrofluoric acid (FH) | Corrosive, Toxic – effects the respiratory tract |
| Sulfuric Acid (SO4H2) | Corrosive, Toxic – effects the respiratory tract |
| Ammonia (NH3) | Toxic – effects the respiratory tract |
| Argon (Air) | Replaces oxygen Choking |
| Chlorine (Cl) Toxic | Aggressive to eyes and affects the respiratory tract |
| carbon dioxide (CO2) | Toxic Replaces Oxygen – Choking |
| Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) | Toxic – severely affects the respiratory tract |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | Toxic – severely affects the respiratory tract |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Toxic – high risk of loss of consciousness and asphyxiation |
| Nitrogen (N) | Replaces oxygen – choking |
| Ozone (O2) | Toxic – effects the respiratory tract |
| Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) | High toxicity – severely affects the airways and may cause lung failure |
Fire and Explosion Hazards
| Flammable atmosphere | Explosive atmosphere |
| Fuel – flammable products and vapors present in confined space or formed by chemical reactions | Causes – high concentrations of combustible vapors, pressure equipment, and high oxygen concentrations |
| Flashpoints – electrical discharges, welding and cutting jobs, human error | Flashpoints – electrical discharges, welding and cutting jobs, human error |
Environmental Risks
- Lack of or insufficient lighting
- Excessively low or high temperature
- High humidity
- A high volume of dust.
Biological Risks
- Bacteria
- Virus
- Fungi
- Pests
In addition to the risks mentioned above, due to possible unfavorable configurations and access characteristics, confined spaces may also entail additional risks inherent in the increased difficulty of rescuing the workers involved in confined space work. See also How to rescue in confined space







