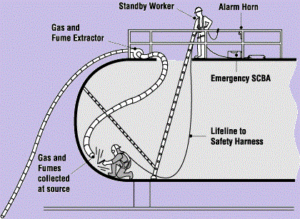
Confined space definition and dangers
Confined space definition and dangers? Large industrial installations or machines require regular maintenance, cleaning or inspection. Common examples of applications are cleaning or inspection of sewers, maintenance of silos and storage tanks or checking of cargo or fuel tanks on ships.
You often enter a tight space with little air circulation, narrow passages, and extra dangers. You call this a confined space. But by no means, every tight space is a confined space and not every confined space is completely walled.
Accidents occur regularly because employees do not correctly assess the risks in such a place. That is why we give you the most complete definition of a confined space. We then discuss the 8 most common risks when entering.
WHAT IS A CONFINED SPACE
A confined space is not intended for human occupancy or continuous residence, has an enclosed nature, a potentially dangerous atmosphere and is difficult to access i.e. has limited access.
Let us, therefore, look closely at these points.
Not intended for a continuous stay or human occupancy.
You must avoid a confined space as much as possible.
When your employees have to enter a confined space, this is an exception to the rule and you actually enter a different workplace. Place sufficient signage and place pictograms to ensure that none of your employees enter a confined space without written approval e.g. permit to work.
If machines or other installations still require maintenance or inspection, keep the staying time and the number of employees in the confined space as low as possible.
Confined space is closed & sometimes it might not. Often you do not immediately recognize the differences.
For example, an open slot or pit or excavation becomes a confined space when there is not enough air circulation. Gases that are heavier than air (for example, carbon dioxide, Hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide) thus have the opportunity to accumulate on the low level on the soil inside the pit, slot or excavation.
Even spaces that are partially walled are technically a confined space. For example, there are cases where a nitrogen leak on one side of an open tent or place has killed many people.
Limited or difficult access
For the most part, you recognize a confined space at the opening or location. Openings are usually very narrow (45 cm diameter) and it is difficult to move through them.
Getting tools through the opening is just as problematic and certainly, life-saving resources (for example fall protection) are not a piece of cake.
In addition, you also have larger openings such as loading spaces of a ship. They create other problems. You need ladders or lifting equipment to enter the room and in emergencies, it is difficult to escape from these rooms.
A dangerous atmosphere
Asphyxiation, fire or explosion are the most common causes of accidents in confined spaces.
You actually look at it this way: the dangers in the confined space determine whether it is decided, not the confined space itself.
Gasses inside confined spaces should be checked on at least 4 levels
- Before opening the confined space e.g. outside the cover of a manhole before opening it. Might be there is a chance or any gas leaking from an inside manhole into the outside atmosphere it will give an idea that the confined space has which gases inside.
- Then check the gasses from the upper level
- Middle level
- Lower level
What is the confined space definition and dangers? Gasses should be checked on different levels and depths but it depends upon the depth of the excavation. But always remember that do not ever assume that there would be no gasses inside the confined space it is your legal duty to check the gasses prior to entry inside the confined space.
You will check the following 4 gasses in the confined space:
See Also How to check gas inside confined space with Ventis MX4
- Oxygen level must be between 19.5% to 23.5% and it is measured in percentage.
- Hydrogen sulfide it must be less than 10PPM it is measured in part per million
- Carbon monoxide it must be less than 35 PPM it is measured in part per million
- LEL it must be less than 10% by volume. Methane, Ethane, propane, I-butane, n-butane, pentane, etc. are measured under LEL.
There are Lower and Upper explosive limits also we will discuss it later on.
Different risks usually occur simultaneously. Not only dangerous gases but also injuries from bumps or moving machine parts are risks that regularly occur.
Prior to entry in Confined Space things to be checked carefully

- Method statement and risk assessment
- Permit to Work
- 3rd party training of Entrants and Standby person and Rescue team
- Gas testing by an authorized and competent gas tester.
- Entry log
- 3rd party certified rescue devices e.g. winch, tripod stand, full-body harness, etc.
- certified multi-gas monitors
- certified personal gas monitors
- area barricading
- area signages
- pre-task briefing
- job safety card or STARRT card
- Tool Box talks
- competent works
- firefighters
- first aiders
- stand by ambulance
- AED & resuscitation equipment
- information instruction training and supervision
- always ask when in doubt
DANGERS WITH RESPECT TO AN ENCLOSED SPACE
Asphyxiation
Asphyxiation is by far the most important risk in a confined space. Normal air consists of 78% nitrogen gas, 21% oxygen gas, and 1% argon. If the oxygen concentration falls below 18%, there is a risk of suffocation. Moreover, your senses do not perceive what is happening to you. You fall into intoxication and you no longer recognize the dangers. Oxygen deficiency is caused by insufficient ventilation inside confined space. The oxygen present decreases due to chemical or biological reactions. Confined space definition and dangers
For example, Drying paint or poorly blocked pipes release gases that drive the oxygen away. Some welding processes also entail hazardous gases. If you can’t drive it away, it becomes a risk. The presence of inert gases such as nitrogen or carbon dioxide also causes oxygen deficiency. In some cases, you can prevent a fire or explosion hazard with this (because the amount of air may not be too high).
Fire and explosion hazard
If the oxygen concentration is higher than 21%, there is a risk of fire or explosion. In a confined space with, for example, 30% oxygen, one spark is sufficient for cotton overall within a minute. One of the most common causes of too high a concentration of oxygen is incorrect to use of welding or cutting equipment. Types of fire extinguishers and their suitability
Flammable and explosive substances that can occur in confined spaces are, for example, paints, solvents, (remnants of) materials and cleaning rags, gas released or oxygen from improperly sealed gas and oxygen bottles or remnants of the contents of the confined space. Sparks are caused by the discharge of static electricity or by the use of tools that are not antistatic. what are classes of fire
Exposure to hazardous chemicals
Poisoning symptoms occur when you are exposed to hazardous substances. Often health effects from exposure occur immediately, but sometimes the effects only become noticeable for a longer period of time. These substances penetrate your body through the lungs, mouth or through your skin. Cleaning agents, paintwork, electric welding or work on contaminated soil can release hazardous substances or gases.
Electrocution
Electrocution occurs when you touch objects under electrical voltage. When power tools or cables are damaged, such as pinching, the risk of electrocution is high. Even when damaged cables make contact with metal parts or walls of a confined space, they are also put under tension.
Heat stress
Heat stress occurs when you are no longer able to control your body temperature due to high temperatures and humidity. The causes are varied: radiant heat, humidity or protective clothing (gas suits). Your body heats up and this creates “heat-related illness or diseases” such as heat exhaustion or heat cramps.
If you work in an extreme heat area (for example engine compartment), it is important to drink enough water to compensate for perspiration (every 15 to 20 minutes). See also How to make confined space entry procedure
Crushing
As we have explained earlier, the opening of a confined space is often narrow.
Pinching can then occur due to:
Narrowed in and outputs
Limited space in the workplace
Transport of material
Use of special PPEs such as gas-tight coveralls that take up a lot of space, but are crucial.
Noise
Devices such as compressed air tools or welding equipment generate a lot of noise. Due to the high resonance (resounding of sound) in a confined space, you quickly get above 80 decibels. Good hearing protection is therefore certainly in place when entering a confined space.
Stumbling and falling
What is confined space definition and dangers You often have to work at heights because the access to the confined space is upstairs? Scaffolding or ladders are also regularly used inside the confined space. Wearing fall protection and inspecting handrails is therefore of crucial importance when entering a confined space.
All workers who are involved in working at scaffolding must be informed through toolbox talked that they can not use any ladder or access to the scaffolding if the tag is Red. See also What are fall protection systems for scaffolders
A red tag means that the scaffold is not safe for use either it is incomplete or is under construction. Employees can only access the scaffold if the tag is green and is inspected by a third-party certified “Scaffolding inspector”. When you work at different levels, tools, loose objects or debris can fall. So be sure to put on a helmet to protect yourself against falling objects.
Slippery Surfaces
Workers can face slip trips and falls hazards inside confined space which can lead to serious injuries. What is confined space definition and dangers A confined space prior to entry must be cleaned from all kinds of slipping hazard e.g. sludge or spills etc? Good housekeeping must be maintained all the time inside confined space.
Poor illumination
Slips and trips can also be due to poor illumination inside the working area so proper illumination must be provided to the workers. To avoid falls caused by poor illumination.
Water accumulation
If the water is present inside the confined space e.g. manholes etc the water must be removed prior to entry because it can cause drowning of workers and the other hazard which is connected with hydrogen sulfide is that if the water is present inside confined space then the Hydrogen sulfide will mix with the water and will not be detectable. Excavation safety guide with photos
CONCLUSION
As you can understand now, a confined space is a very risky and unstable environment. In addition to these dangers, there are undoubtedly risks that did not occur here. You pay a lot of attention to this in your risk analysis and look for the best solution. What is confined space definition and dangers Discuss everything together with your colleagues, identify the potential dangers and practice enough! Every confined space is different and unfortunately, one solution for entry does not yet exist. How safety officers can save themselves from the court in case of an accident